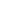
A steel pipe whose outer diameter to wall thickness ratio is less than 20 is called a thick-walled steel pipe.
Mainly used as petroleum geological drilling pipes, cracking pipes for the petrochemical industry, boiler pipes, bearing pipes, high-precision structural pipes for automobiles, tractors, and aviation, etc.
The manufacturing process of seamless steel pipe 1. Hot rolling (extruded seamless steel pipe): round tube billet → heating → piercing → three-roll cross rolling, continuous rolling or extrusion → tube removal → sizing (or reducing) → cooling → Straightening→hydraulic test (or flaw detection)→marking→warehousing
The raw material for rolling seamless steel pipes is round tube blanks, which are cut by a cutting machine into billets with a length of about 1 meter, and sent to the furnace for heating by a conveyor belt. Billet is fed into the furnace to heat, the temperature is about 1200 degrees Celsius. The fuel is hydrogen or acetylene. The temperature control in the furnace is a key issue. After the round tube is out of the furnace, it must be pierced through a pressure piercer. Generally, the more common piercer is the cone roll piercer. This kind of piercer has high production efficiency, good product quality, large perforation diameter expansion, and can wear a variety of steel types. After piercing, the round tube billet is successively cross-rolled, continuously rolled, or extruded by three rolls. After extrusion, the tube should be taken off for sizing. Sizing by high-speed rotary cone drill holes into the billet to form a tube. The inner diameter of the steel pipe is determined by the length of the outer diameter of the drill bit of the sizing machine. After the steel pipe is sized, it enters the cooling tower and is cooled by spraying water. After the steel pipe is cooled, it will be straightened. After straightening, the steel pipe is sent to the metal flaw detector (or hydraulic test) by the conveyor belt for internal flaw detection. If there are cracks, bubbles, and other problems inside the steel pipe, they will be detected. After the quality inspection of steel pipes, strict manual selection is required. After the quality inspection of the steel pipe, paint the serial number, specification, production batch number, etc. with paint. And hoisted into the warehouse by crane.
2. Cold drawn (rolled) seamless steel pipe: round tube blank→heating→perforation→heading→annealing→pickling→oiling (copper plating)→multi-pass cold drawing (cold rolling)→blank tube→heat treatment→straightening → Hydrostatic test (flaw detection) → Marking → Storage.
Production classification of seamless steel pipes – hot-rolled pipes, cold-rolled pipes, cold-drawn pipes, extruded pipes, jacked pipes
1. Structural seamless steel pipes (GB/T8162-1999) are seamless steel pipes used for general structures and mechanical structures.
2. Seamless steel pipe for fluid transportation (GB/T8163-1999) is a general seamless steel pipe used to convey fluids such as water, oil, and gas.
3. Seamless steel pipes for low and medium pressure boilers (GB3087-1999) are used to manufacture superheated steam pipes, boiling water pipes for low and medium pressure boilers of various structures, superheated steam pipes, large smoke pipes, small smoke pipes and arch bricks for locomotive boilers High-quality carbon structural steel hot-rolled and cold-drawn (rolled) seamless steel pipes for pipes.
4. Seamless steel pipes for high-pressure boilers (GB5310-1995) are high-quality carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless heat-resistant seamless steel pipes for the heating surface of water tube boilers for high pressure and above.
5. The high-pressure seamless steel pipe for chemical fertilizer equipment (GB6479-2000) is a high-quality carbon structural steel and alloy steel seamless steel pipe suitable for chemical equipment and pipelines with a working temperature of -40~400°C and a working pressure of 10~30Ma.
6. Seamless steel pipes for petroleum cracking (GB9948-88) are seamless steel pipes suitable for furnace tubes, heat exchangers, and pipes in petroleum refineries.
7. Steel pipes for geological drilling (YB235-70) are steel pipes used by geological departments for core drilling. According to their uses, they can be divided into drill pipes, drill collars, core pipes, casing pipes, and sedimentation pipes.
8. Seamless steel pipes for diamond core drilling (GB3423-82) are seamless steel pipes used for drill pipes, core rods, and casings for diamond core drilling.
9. An oil drilling pipe (YB528-65) is a seamless steel pipe used for oil drilling with inner or outer thickening at both ends. There are two types of steel pipes: threaded and non-threaded. The threaded pipes are connected with joints, and the non-threaded pipes are connected with tool joints by butt welding.
10. Carbon steel seamless steel pipes for ships (GB5213-85) are carbon steel seamless steel pipes for the manufacture of Class I pressure-resistant piping systems, Class II pressure-resistant piping systems, boilers, and superheaters. The working temperature of the carbon steel seamless steel pipe wall does not exceed 450°C, and the working temperature of the alloy steel seamless steel pipe wall exceeds 450°C.
11. The seamless steel pipe for automobile half-shaft casing (GB3088-82) is a hot-rolled seamless steel pipe of high-quality carbon structural steel and alloy structural steel for the manufacture of automobile half-shaft casing and drive axle casing shaft pipe.
12. High-pressure fuel pipe for diesel engine (GB3093-86) is a cold-drawn seamless steel pipe for manufacturing high-pressure pipe of diesel engine injection systems.
13. Precision inner diameter seamless steel tubes for hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders (GB8713-88) are cold-drawn or cold-rolled precision seamless steel tubes with precise inner diameters for the manufacture of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders.
14. Cold-drawn or cold-rolled precision seamless steel pipe (GB3639-83) is a cold-drawn or cold-rolled precision seamless steel pipe with high dimensional accuracy and good surface finish for mechanical structures and hydraulic equipment. The use of precision seamless steel pipes to manufacture mechanical structures or hydraulic equipment can greatly save machining hours, improve material utilization, and help improve product quality.
15. Structural stainless steel seamless steel pipe (GB/T14975-1994) is a hot-rolled ( extrusion, expansion) and cold-drawn (rolled) seamless steel tube.
16. Stainless steel seamless steel pipes for fluid transportation (GB/T14976-1994) are hot-rolled (extruded, expanded) and cold-drawn (rolled) seamless steel pipes made of stainless steel for fluid transportation.
17. Special-shaped seamless steel pipe is a general term for seamless steel pipes with cross-sectional shapes other than round pipes. According to the shape and size of the cross-section of the steel pipe, it can be divided into special-shaped seamless steel pipes with equal wall thickness (code-named D), special-shaped seamless steel pipes with different wall thickness (code-named BD), and special-shaped seamless steel pipes with variable diameter (code-named BJ). Special-shaped seamless steel pipes are widely used in various structural parts, tools, and mechanical parts. Compared with round pipes, special-shaped pipes generally have a larger moment of inertia and section modulus, and have greater bending and torsion resistance, which can greatly reduce the structural weight and save steel.
Generally, seamless steel pipes are made by hot rolling or cold rolling of high-quality carbon structural steels such as 10, 20, 30, 35, 45, 16Mn, 5MnV, and other low-alloy structural steels, or 40Cr, 30CrMnSi, 45Mn2, 40MnB and other combined steels. Seamless steel pipes made of low carbon steel such as 10 and 20 are mainly used for fluid conveying pipelines. Seamless steel pipes made of medium carbon steel such as 45 and 40Cr are used to manufacture mechanical parts, such as stressed parts of automobiles and tractors. Generally, seamless steel pipes should be tested for strength and flattening. Hot-rolled steel pipes are delivered in a hot-rolled or heat-treated state; cold-rolled steel pipes are delivered in a heat-treated state. Seamless steel pipes for low and medium-pressure boilers: used to manufacture various low and medium-pressure boilers, superheated steam pipes, boiling water pipes, water wall pipes, and superheated steam pipes for locomotive boilers, large smoke pipes, small smoke pipes, and arch brick pipes, etc.
Hot-rolled or cold-rolled (dial) seamless steel pipes are made of high-quality carbon structural steel. It is mainly made of No. 10 and No. 20 steel. In addition to ensuring the chemical composition and mechanical properties, hydrostatic tests, crimping, flaring, and flattening tests are required. Hot rolling is delivered in a hot-rolled state, and cold rolling (dial) is delivered in a heat-treated state.
18. GB18248-2000 (seamless steel pipe for gas cylinders) is mainly used to make various gas and hydraulic cylinders. Its representative materials are 37Mn, 34Mn2V, 35CrMo, etc.
Calculation formula and examples for seamless steel pipes: (kg/m) W= 0.02466 × S (D – S) D= outer diameter S= wall thickness
Find the weight per m of a seamless steel pipe with an outer diameter of 60 mm and a wall thickness of 4 mm. Weight per m = 0.02466 × 4 × (60 –4 ) = 5.52kg 9. An oil drilling pipe (YB528-65) is a seamless steel pipe used for oil drilling with inner or outer thickening at both ends. There are two types of steel pipes: threaded and non-threaded. The threaded pipes are connected with joints, and the non-threaded pipes are connected with tool joints by butt welding.
GB3088-82) is a hot-rolled seamless steel pipe of high-quality carbon structural steel and alloy structural steel for the manufacture of automobile half-axle casings and drive axle housing shaft pipes
10. Carbon steel seamless steel pipes for ships (GB5213-85) are carbon steel seamless steel pipes for the manufacture of Class I pressure-resistant piping systems, Class II pressure-resistant piping systems, boilers, and superheaters. The working temperature of the carbon steel seamless steel pipe wall does not exceed 450°C, and the working temperature of the alloy steel seamless steel pipe wall exceeds 450°C.
11. The seamless steel pipe for automobile half-shaft casing (GB3088-82) is a hot-rolled seamless steel pipe of high-quality carbon structural steel and alloy structural steel for the manufacture of automobile half-shaft casing and drive axle casing shaft pipe.
12. High-pressure oil pipes for diesel engines (GB3093-2002) are cold-drawn seamless steel pipes for the manufacture of high-pressure pipes for diesel engine injection systems.
13. Precision inner diameter seamless steel tubes for hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders (GB8713-88) are cold-drawn or cold-rolled precision seamless steel tubes with precise inner diameters for the manufacture of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders.
The biggest difference between thick-walled steel pipes and thin-walled steel pipes is the thickness of the steel pipe wall
Generally speaking, thin-walled steel pipes are cold-drawn technology, while thick-walled steel pipes generally use hot-drawn technology. If it is distinguished by measurement units, then it is generally believed that a wall thickness/pipe diameter equal to 0.02 is a thick-walled steel pipe, and Watershed for thin-walled steel pipes, wall thickness/pipe diameter less than 0.02
The largest is the thin-walled steel pipe, and the larger one is the thick-walled steel pipe. In terms of use, thin-walled steel pipes are mostly used for pipelines. And thick-walled steel pipes are mostly used as bad materials for hollow parts. Used on pressure-bearing and important pipelines.
Regulations and applications of thick-walled steel pipes in engineering
1. Corresponding regulations and various regulations for the actual selection and use of thick-walled pipe fittings
When thick-walled pipe fittings are selected or used, they must first follow the relevant regulations and specifications, especially in occasions where extremely or highly hazardous fluid media, flammable media, and high-pressure gas are transported. Under this premise, the type of pipe fittings is mainly determined according to the purpose and conditions of use (pressure, temperature, fluid medium). The relevant regulations/standards are mainly listed below for reference only.
1) Special Equipment Safety Supervision Law;
2) List of special equipment safety inspection regulations;
3) Pressure pipeline safety management and supervision regulations;
4) Special equipment quality supervision and safety supervision regulations;
5) Special equipment design/manufacture/installation supervision and management regulations (draft);
6) Pressure pipeline safety technical supervision regulations (draft);
7) Safety technical specifications for industrial metal pipelines (draft);
2. Determination of the strength grade of pipe fittings
1) For pipe fittings whose grade is indicated by nominal pressure or specified pressure-temperature rating, the pressure-temperature rating specified in the standard shall be used as the reference, such as GB/T 17185;
2) The standard only stipulates the nominal thickness of the straight pipe connected to it, and its applicable pressure-temperature rating is determined according to the standard pipe grade specified in the standard, such as GB14383~GB14626.
3) For pipe fittings that only specify the external dimensions in the standards, such as GB12459 and GB 13401, their bearing strength should be determined through confirmatory tests. 4) For others, pressure design or analytical analysis shall be carried out by relevant regulations to determine the use standard. In addition, the determination of the strength grade of the pipe fittings should not be lower than the pressure under the most severe working conditions that the entire piping system may encounter during operation.
3. Safety and economy
In addition to the above-mentioned structural types of pipe fittings used in actual piping engineering, there are other structural types of pipe fittings to meet the requirements of various working conditions, especially special working conditions. In engineering design or selection, the higher the strength grade of pipe fittings, the higher the safety, but the greater the cost of the project, it will cause unnecessary waste.
From the perspective of economic benefits, while meeting the requirements of engineering design and reducing costs as much as possible, it is often easy to result in a small number of selected pipe fittings as a whole, which is not conducive to the management and regulation of on-site construction materials and the needs of design changes. material substitution etc. Therefore, the selection of pipe fittings should combine safety and economy, and it is advisable to reduce the variety of pipe fittings as much as possible. In addition, factors such as the conditions of on-site construction, the level of construction, and the procurement cycle of pipe fittings should also be given the necessary attention in the selection of pipe fittings. In specific cases, the possibility of adopting reinforced pipe joints, mitered elbows, and on-site bending of small-diameter pipes should also be considered.
At the same time, it is also necessary to understand the production capacity, products, and market supply of pipe fittings manufacturers.
4. Problems in the selection standard of pipe fittings
1) Domestic pipe fitting standards are not perfect, and unmatched pipe fitting standards should include pipe fitting type parameter standards and pipe fitting material standards. However, the material standards are either incomplete, or lack quality and technical requirements such as cargo requirements, inspection and batching rules, and quality certification. The standards of pipe fitting materials are poorly matched and are often formulated from their standpoints and angles, rather than from the entire standard system of pressure piping. For the selection in engineering, there are pipe standards, but there is no corresponding standard for forgings or castings. The reality is that the standard for forgings of pipe fittings borrows the standard for forgings of pressure vessels, without considering the differences between the two, such as welding, film inspection, and other regulations.
2) The standard level of pipe fittings varies greatly, and the content lacks consistency and systematicness, so that there are contradictions in the connection, causing inconvenience in use.
3) There is no type test standard for pipe fittings. Only the GB12459 and GB13401 standards stipulate the pressure calculation for the burst test of steel butt-welded seamless steel pipe fittings and steel plate butt-weld pipe fittings. Other types of test standards or implementation standards to ensure the quality of pipe fittings manufacturing No.
The weight formula of seamless steel pipe: [(outer diameter-wall thickness)*wall thickness]*0.02466=kg/m (weight per meter)
Post time: Aug-29-2023