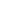
What are OCTG pipes? Oil country tubular goods are pipes used for onshore and offshore oil & gas upstream operations (extract oil and gas from the wellbore). OCTG pipes may be classified into three main families: drill pipes (to perforate the soil and reach the reserve), casing pipes (to consolidate the well and prepare it for the actual extraction), and tubing pipes (to extract the product from the ground to the surface). API 5CT is the reference specification for OCTG pipes.
TYPES OF OCTG PIPE
First, OCTG is the acronym of “Oil Country Tubular Goods” – i.e. pipes for oil (and gas) extraction from the soil. The three main OCTG pipe types are:
Casing pipes are used to stabilize the wellbore. A casing pipe is subject to axial tensions and to internal pressures generated by the pumped oil or gas, by their heavyweight and the external pressures coming from the surrounding rocks
Tubing pipes are tubular goods through which the oil or gas is transported from the wellbore to the surface. Tubing segments are generally around 30′ long with a threaded connection on each end (standard or premium connections are available)
Drill pipes are heavyweight seamless tubular that rotate the drill bit and circulates the drilling fluid. Pipe segments of 30′ are coupled with tool joints. Drill pipe is subject to high torque by drilling, axial tension by their weight, and internal pressure due to the purging of the drilling fluid. Additionally, alternating bending loads due to non-vertical or deflected drilling may be superimposed on these basic loading patterns
The API 5CT specification covers seamless and welded casing and tubing pipes for upstream operations (pipes that belong to the OCTG family, as illustrated above).
OCTG “CASING” PIPES
Function
OCTG casing pipes are a key structural component for an oil & gas well and have the following scope:
Keep the borehole stability in the well
Prevent the bore contamination from water sands
Prevent water from producing formations
Exercise a tight control of the wellbore pressures during the drilling, production, and repair operations
Casing pipes are used to install:
Blowout Preventers (BOP)
Other wellhead equipment necessary to extract hydrocarbons
Production tubing and packers
Casing pipes are also one major individual component of the overall cost of the well, therefore the correct selection of the casing size, materials, connectors, and depth shall be at the top of design engineers (for cost and efficiency reasons).
The six basic types of casing strings are:
- Conductor Casing
- Surface Casing
- Intermediate Casing
- Production Casing
- Liner
- Liner tieback casing
Oilfield casing pipes are positioned into the wellbore and cemented in place to secure both subsurface formations and the wellbore from collapsing, also to enable drilling mud to circulate and extraction to take place.
The strict quality requirement for steel is due to the harsh working conditions of the casing.
The steel product should be produced and checked in accordance with special standards or specifications. ISO 11960 and API Spec 5CT have specified the steel product standards of the casing.
Dimensions and Materials
Casing pipes are available in a diameter range 4 1/2 to 20 inches, and in the following materials: H-40, J-55, K-55, N-80, L-80/C, 90/T, 95, P110, Q-125 – as discussed in more detail below.
End Connection Types
The main types of connections for casing pipes are STC (short threads), LTC (long threads), BTC (buttress threads) and premium gas-tight connections.
OCTG “TUBING” PIPES
Function
Tubing pipes are used to bring oil and gas from the underground reserves up to the field for further processing.
Tubing pipes need resistance to mechanical stress as they are subject to very high loads and deformations during the production operations.
In addition, tubing pipes sizes should be properly calculated to support the expected oil and gas flow from the ground to the surface (a too-small diameter would decrease the production rate and the return on investment on the wellbore licenses, whereas too large tubing would generate non-recoverable costs due to the greater amount of steel used for the bore construction vs. the actual requirement (steel for the casing and tubing pipes).
Sizes and Materials
Tubing pipes are manufactured in seamless and welded execution, in the size range of 1.050 to 5 1/2 inches (consult this article to see the AP5CT tubing pipes sizes) and in the following material grades: H-40, J-55, K-55, N-80, L-80, C-90, T-95, P-110, Q-125 (more details about API 5CT tubing materials are in this article).
End Connections
The main types of connections for tubing pipes are NUE (non-upset), EUE (external upset) and premium. Corrosion resistance under sour service conditions is a very important OCTG characteristic, especially for casing and tubing.
Post time: May-09-2022